About Sterile Pharmaceuticals
Sterile pharmaceuticals include injectable drugs administered by injection, dialysis agents administered through dialysis, and eye drops administered to the eye. Direct containers in contact with the drug have functions to maintain the quality of the drug and to ensure user convenience. These containers include ampoules, vials, cartridges, infusion bags, pre-filled syringes (PFS), blow-fill-seal (BFS), form-fill-seal (FFS), and plastic containers. Sterile pharmaceuticals are manufactured using either terminal sterilization methods or aseptic processing methods to ensure sterility. When handling various containers such as vials and syringes, the supply form of direct containers called NEST, where pre-washed and sterilized direct containers are set in dedicated cases, is sometimes used. In such cases, devices like filling machines are also dedicated to NEST, but they feature easy container switching. Filled products are packed in single or multiple layers of films or paper, labeled with legally mandated information (such as lot numbers, expiration dates, and GS1 barcodes), and maintain the quality of the product during transportation and prevent errors and ensure convenience during use.
Example of a Sterile Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Process
The following diagram illustrates the process flow of a vial product using the aseptic method as an example of a sterile pharmaceutical.
Example of Process Flow Diagram:
Vial Product Using Aseptic Method
- Weighing of raw materials, preparation and processes from washing of containers filling/stoppering/sealing, these processes are conducted in a clean room controlled for appropriate particle count, temperature, and humidity to prevent microbial and foreign matter contamination. Particularly, the filling and stoppering processes are performed in grade A cleanliness environments, classified as critical areas.
- Vials are depyrogenized through a dry heat sterilization tunnel, while rubber stoppers are washed and sterilized using dedicated equipment. The preparation solution is supplied to the filling device via a sterile filtration filter.
- Sealed vials are inspected for external and internal foreign substances using visual inspection machines, and quality tests, including sterility testing of sampled products, are conducted.
- Filled products that pass the quality tests are labeled with information such as lot numbers and expiration dates. They are then packed into carton printed with the necessary information. Lots that pass final testing are shipped.
Key Points of Sterile Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Equipment
Manufacturing Process and Cleanliness Class/Grade Management Concepts
Filling has traditionally been conducted in an aseptic room, however, when introducing new equipment, it is increasingly common to incorporate isolator and Restricted Access Barrier System (RABS) technologies to completely isolate from operator contact, which is one of the highest contamination risks, into grade C/D environments. Surrounding equipment such as glove leak testers, decontamination devices, and particle monitoring systems are necessary. Coordination with the air conditioning system is also required for decontamination.
Operator Safety
With the increase in high potency product such as biopharmaceuticals, in addition to product quality, containment performance using isolators equipped with HEPA filters in preparation and filling equipment exhausts are demanded from the perspective of operato safety. The design of pressure differentials and airflow inside and outside the isolators and filling rooms during operation and decontamination is necessary. Additionally, external washing devices for cleaning the outer surfaces of containers after filling may be introduced as needed.
Leak Testing/Integrity Assurance

For ensuring the integrity of containers, in the case of vials, the opening of the empty vial is inspected with a camera to prevent leaks from the rubber stopper area, and various parameters of the rubber stoppering and sealing devices are monitored for each vial to ensure integrity. Automatic container leak testers from multiple companies can be chosen based on the risk. In the case of containers sealed by melting such as ampoules, 100% inspection is conducted using dry or wet pinhole inspection machines.
Risk Mitigation for Foreign Matter Contamination

Foreign matter contamination poses a significant quality risk, so preventive measures against foreign matter contamination are taken with each equipment until the container is sealed. Monitoring the cleaning functions of washing machines is also necessary. In the event of glass container breakage at the filling supply section, it is important to introduce detection devices and design so that surrounding containers can be recovered through gloves. When introducing visual inspection machines for foreign matter after filling, it is necessary to confirm with the manufacturer in advance that the equipment can distinguish and inspect external foreign matter from bubbles in the solution or the content of the preparation. Minimize the number of false rejections, confirm the detected foreign matter and converting the results into data is to help reduce foreign matter contamination.
Aseptic Connection Devices
Rubber stoppers are fed in the vessel with RTP (rapid transfer port) and washed, sterilized and dryed in the vessel on the washing and sterilizing equipmant and then the vessel is transported in filling room and connected to the filling isolater with the lifter and rubber stoppers are fed to the stoppering device aseptically. This machine are available from several manufacturers. Considerations need to be given to the size of the vessel, the frequency of washing and sterilization, whether aluminum caps require sterilization, and the method of installing lifters and the available installation space.
Prevention of Medical Accidents, Traceability
To prevent medical accidents caused by misidentification of pharmaceuticals and to ensure traceability, barcode display has been mandated for packaging, requiring printing and inspection device to the packaging process. Additionally, when exporting to overseas, compliance with the labeling regulations of the target country is necessary.
Techniques for Countering Counterfeit Drugs

For high-value and exported abroad drugs, anti-counterfeiting technologies may be applied to labeling materials.
Contamination Prevention Measures

To prevent cross-contamination of different products, enough space and compartmentalization of the production layout as well as equipment specifications facilitating line clearance at the start and end of production are essential. Along with the increase in inspection devices, the amount of rejected products will also rise. Therefore, it is crucial to minimize false detections and to plan sufficient space for handling rejected products in order to eliminate the risk of contaminating defective products. Additionally, shared wash areas for re-cleaning containers and consideration of residual confirmation within product trays used to transport containers are necessary.
Strengths of CM Plus
①Engineering + CM Method
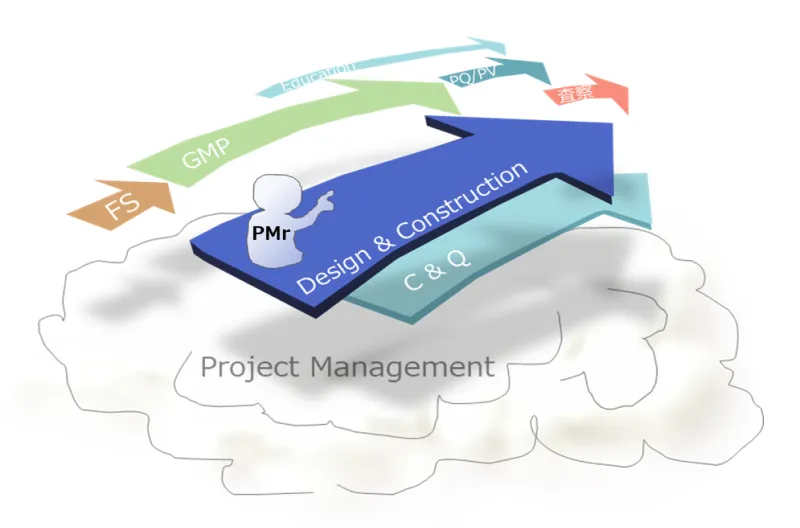
The CM method is a project management system that integrates the client’s perspective with designers to operate and manage projects transparently, ensuring success from the aspects of QCD (Quality, Cost, Delivery) + EHS (Environment, Health, Safety). Professionals, including Construction Managers (CMr) who specialize in management, work on behalf of the client.
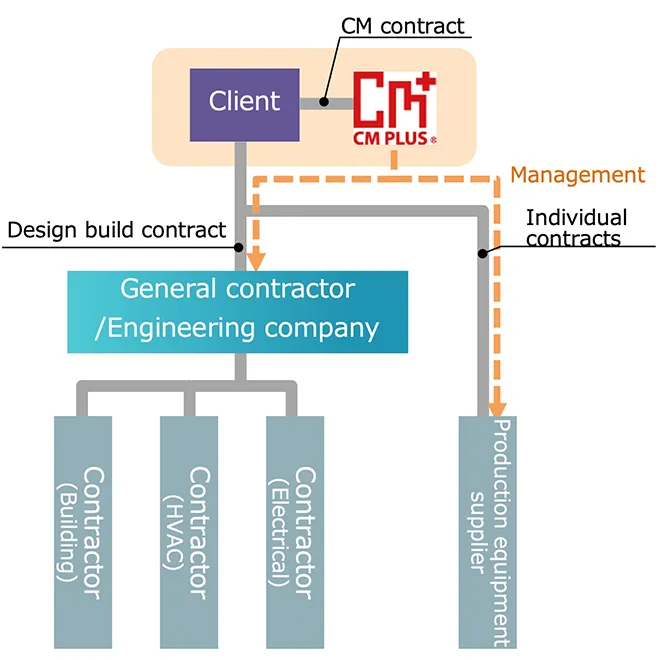
At CM Plus, we conduct engineering (design) in-house. We have engineers who are well-versed in manufacturing processes, equipment and facilities, construction, and manufacturing support facilities (such as electrical systems, HVAC, and utilities). This allows us to oversee the entire facility from the initial planning stages, enabling the construction of integrated and cohesive layout facilities.
②Comprehensive Coordination of Production Equipment and Building Facilities
With a focus on designing from the production process perspective, we execute designs that start from the internal aspects like building production equipment lines, layouts, and internal flow/logistics, leading to the creation of API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient) factories that are in harmony with the production system. Our planning extends to the intangible aspects of the production system as well.
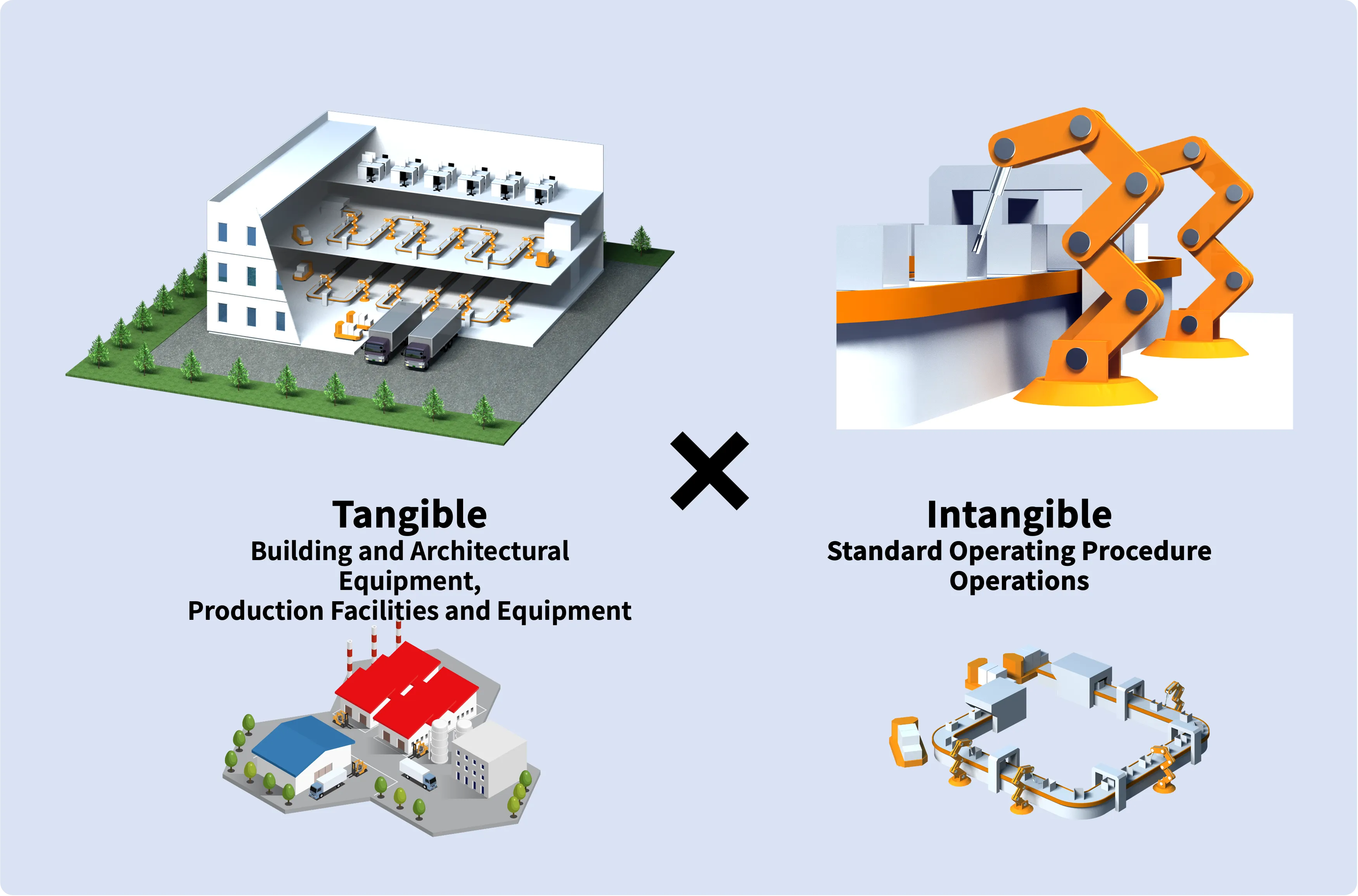
Our team consists of project managers and professional engineers experienced in factory construction across various fields. This allows us to manage the overall project schedule comprehensively, including not only the building and production support facilities but also providing support for the procurement, production management, and coordination of delivery plans of production equipment.

Services provided by CM Plus
Business Concept
We listen to our clients’ requirements and create deliverables such as a list of key equipment, PFD (Process Flow Diagrams), and conceptual layouts to visualize the investment image. Based on the created deliverables, we calculate an approximate investment amount to support investment decisions (Feasibility Study, F/S).

Conceptual Design
In the basic planning (concept design) phase, we compile the client’s requirements and requests through discussions and document them as a User Requirement Brief (URB). We also calculate an approximate project cost based on the contents of the URB.

Basic Design
In the basic design phase, based on the contents of the URB, we create the necessary drawings and specifications for effective solicitation. Specifically, in the process design, we produce PFDs, P&IDs (Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams), data sheets, time schedules (OTS), and equipment specifications required for plant design. We also organize regulations and standards related to facility design and construction, government applications, and environmental conditions, support setting up the project’s master schedule and overall execution plan, and assist with preparations and support for prior coordination with relevant government agencies and utility providers.

Procurement
In the purocurement phase, to build an optimal execution system tailored to the project’s characteristics, we study the order and service divisions and prepare solicitation specifications and procurement specifications based on these considerations. We then solicit quotations from construction companies. We support the client in selecting a construction company by conducting technical evaluations and quotation assessments on the proposals presented by the construction companies and summarizing them in a report.

Detailed Design / Production Management
In the detailed design and manufacturing management phase, we perform design supervision to ensure the construction company and production equipment suppliers reflect the URB, basic design documents, and various regulations in their designs and that progress is on schedule.
Construction and Installation Phase
In the construction and installation phase, we perform construction supervision to ensure that the construction company reflects the URB, URS, detailed design documents, and various regulations in their work, and manage the quality of facilities and equipment. Additionally, a construction manager will reside on-site to manage construction status, progress, and changes from the client’s perspective.

Trial operation
To carry out high-quality and efficient qualification, we provide services that suit the client’s needs, reducing their burden by supporting the creation of a validation master plan and risk assessment from the planning stage and creating protocols for Qualification (DQ, IQ, OQ, PQ), and supporting the execution phase.
Facility Operation
Related Projects
Related Contents
Useful Information
Please refer to the articles on our information dissemination site, “GMP Platform,” which is operated by our company.

“How to Build a Pharmaceutical Plant”
Aggregating expertise for the successful execution of pharmaceutical plant construction projects. From project structuring and basic planning to basic and detailed design, construction, and validation, we provide detailed explanations and key points for each step of the process.